Well, it looks like dire warnings that medical experts have been issuing for months are starting to become reality across parts of the US and Canada. Preliminary data and coronavirus model output are confirming that cooler weather is driving people indoors. As a result, cases are rising in many states and provinces. If you live in any of these states, you need to heed the warnings right now and take all necessary precautions and safety measures to protect yourself and your loved ones.
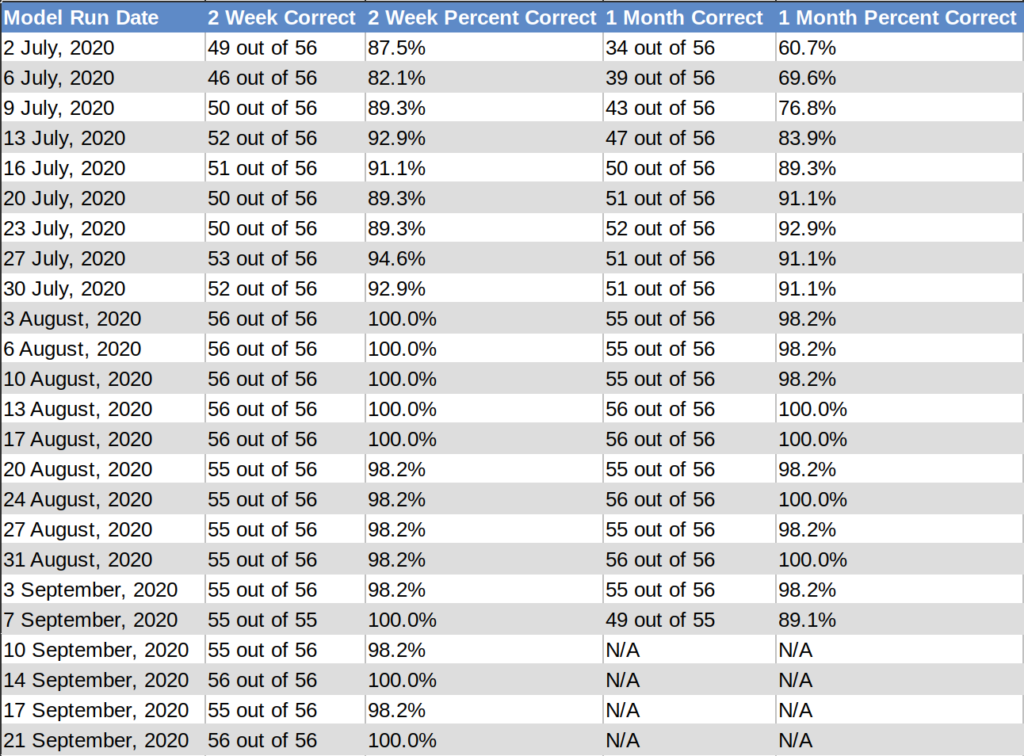
Recent Model Performance
Why am I so concerned? First, my coronavirus model is predicting rather apocalyptic numbers across several states. Second, the model has been deadly accurate with its projections since the beginning of July. My coronavirus model forecasts case counts for the 50 US States and 6 Canadian Provinces at 2 weeks and 1 month from the date of the model run.
A Troubling Precursor: Melbourne, Australia
The most alarming peek into the crystal ball is the significant outbreak of COVID-19 over the 2020 winter in Melbourne, Australia. Starting in late June, a cluster of cases emerged and rapidly spread through the city, peaking in early August before finally tapering off in late September.
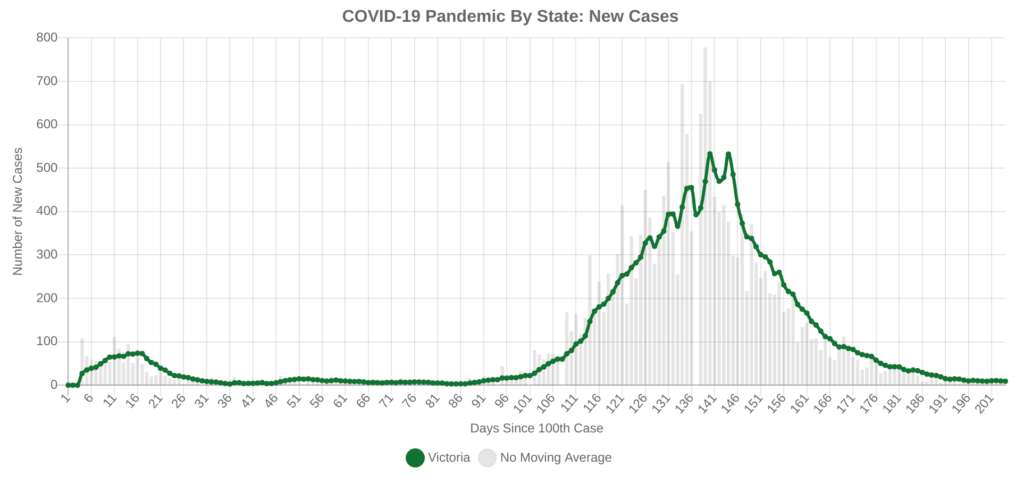
Australian officials deemed the likely cause of the outbreak to be people letting their guard down after Australia’s strict lockdown in April. Does that sound familiar to you?
You know what’s even more concerning about this outbreak, in the context of the United States and Canada? Australia had its outbreak well under control throughout late fall and into the start of winter. The entire country averaged less than 10 new cases per day in early and mid-June. Despite officials putting Melbourne into a very strict lockdown and sealing the entire State of Victoria off from the rest of the country, cases spiked to about 800 per day at their peak in early August, an increase of 2 orders of magnitude, or about 100-fold.
Diving into the Numbers
Let’s do a quick back-of-the-envelope calculation to extrapolate Australia’s outbreak to the United States and Canada. While Australia averaged about 8 new cases per day heading into its winter, the United States is currently averaging 45,000 new cases per day, and Canada is averaging 2,000.
Keep in mind, we’ve still got 2 months to go before the start of our winter in December. It’s also unlikely that either the US or Canada will see the same strict lockdowns and restrictions that were implemented in Victoria.
United States
Base of 45,000 new cases/day
Go up two orders of magnitude
45,000 * 100 = 4,500,000
4.5 million new cases per day
Canada
Base of 2,000 new cases/day
Go up two orders of magnitude
2,000 * 100 = 200,000
200,000 new cases per day
Come on, there’s no way this will actually happen, right? I sure hope not. It’s possible, though not very likely. Remember that everyone said that the US would get a reprieve from the pandemic over the summer, only to see cases spike to 80,000 per day across the Sun Belt.
General Outlook for This Fall and Winter
In many of the states and provinces listed below, you likely will not see the huge spikes like you saw previously in places like New York City, Miami, Melbourne, Los Angeles, and Houston. Instead, it will be a much slower increase due to the lower population density in these states, but the model is showing the potential for the virus to rip through a significant portion of their populations.
In the plots below, I have extended the coronavirus model run out further than one month. Please keep in mind that its accuracy diminishes significantly past the one month mark.
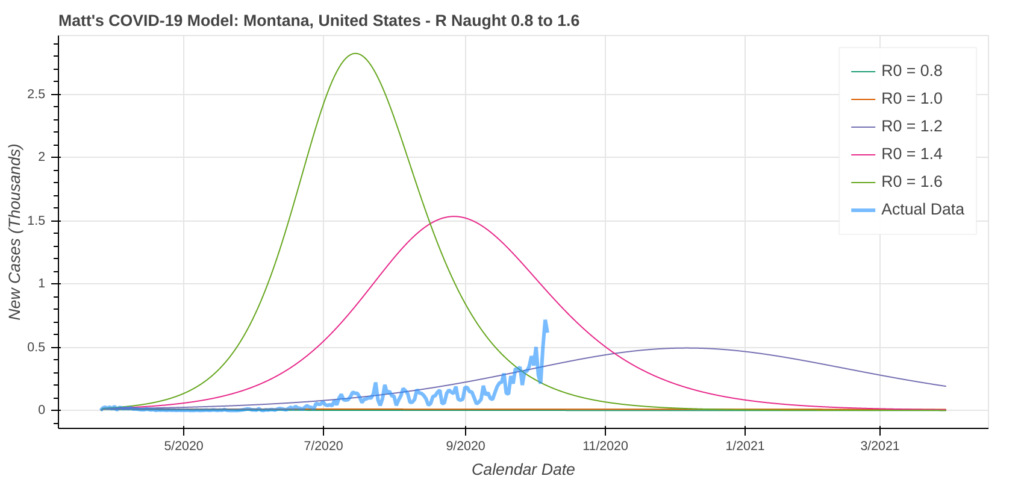
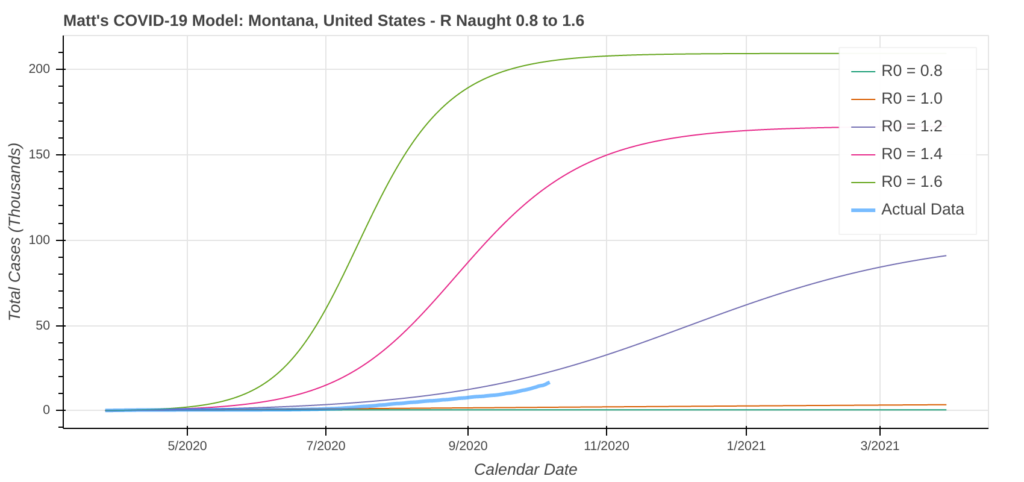
Montana
Montana successfully suppressed the coronavirus over the spring and summer. It is now one of many states in the north-central United States staring down a substantial outbreak of COVID-19. This outbreak will feel much different than the outbreaks across the northeast and the Sun Belt earlier this year.
Instead of a massive and rapid spike, the disease will spread much slower through the community. However, the surge will likely last longer and impact a larger portion of the population than in more populous states.
Previous outbreaks across the northeast and the Sun Belt lasted about 2 to 3 months. Montana’s outbreak will likely last 6 to 8 months due to lower transmission rates. In the worst case scenario, the model expects about 30% of Montanans to come down with COVID-19.
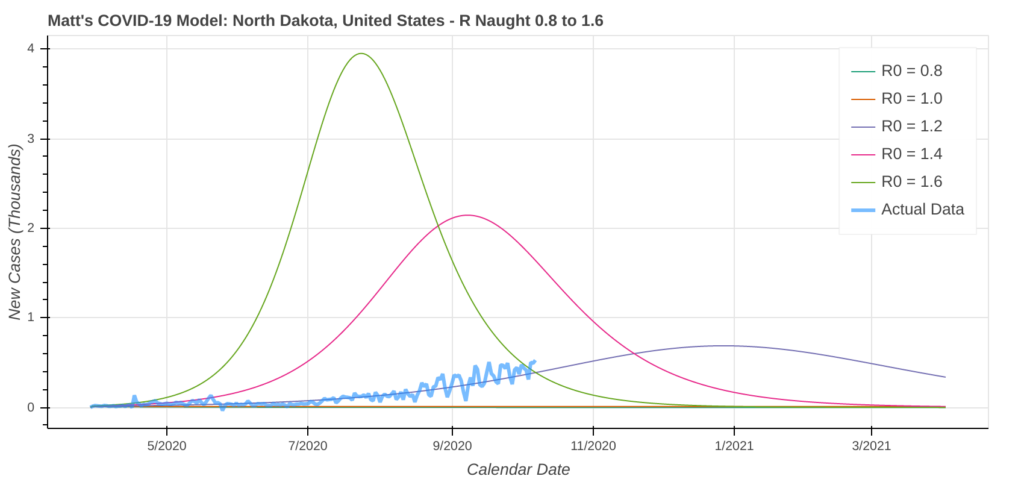
North Dakota
North Dakota has by far the highest average number of new cases per capita for any state since the pandemic began, a distinction that formerly belonged to Arizona. At the peak of its summer spike, Arizona saw a maximum 7-day average of about 510 new cases per million people. North Dakota has seen that number as high as 659 within the past two weeks. The model’s current worst case scenario shows over 60% of North Dakotans contracting COVID-19 by the end of the pandemic.
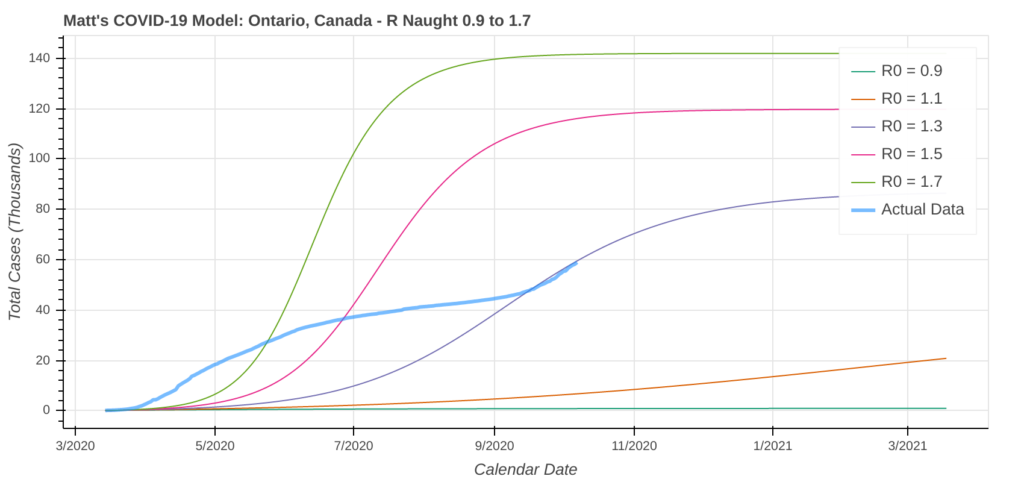
Ontario
The current situation in Ontario is quite fascinating. Over the past few weeks, cases have surged, showing signs of going into a full-blown outbreak, but each time you’ve managed to pull it back from the precipice. Just how long you can keep it up is up to you. There’s still time to prevent a spike.
I am particularly concerned about the heavily populated areas along the Highway 401 corridor, as well as the City of Ottawa, as we get deeper into the fall. It won’t take much to tip things over the edge and look a lot more like neighboring Québec.
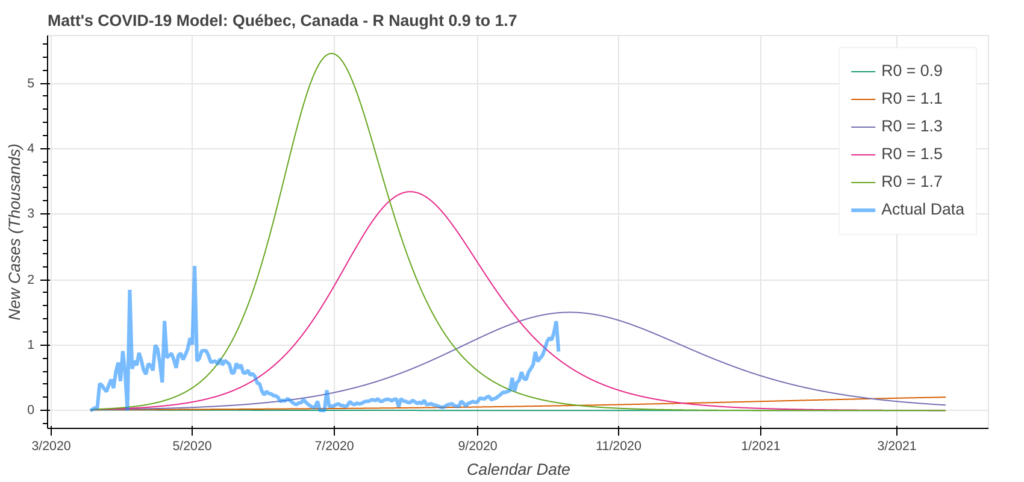
Québec
Québec has been Canada’s epicenter for the majority of the pandemic. After successfully flattening the curve throughout the summer, cases are not just trending upwards as people are driven indoors, they’re accelerating upward. Though I don’t believe any outbreak in Québec will be as bad as ones in the US, without any action, you’ll likely be at 250,000 to 300,000 cases by March, 2021.
Le Québec a été l’epicentre du Canada pour la plupart de la pandémie. Après avoir réussi à aplatir la courbe pendant tout l’été, les cas ne sont pas seulement à la hausse quand tout le monde vient à l’intérieur, ils accélèrent à la hausse. Je ne crois pas qu’une éclosion au Québec sera aussi grave que celles aux États-Unis, mais sans aucune action, vous aurez probablement entre 250,000 et 300,000 cas en mars, 2021.
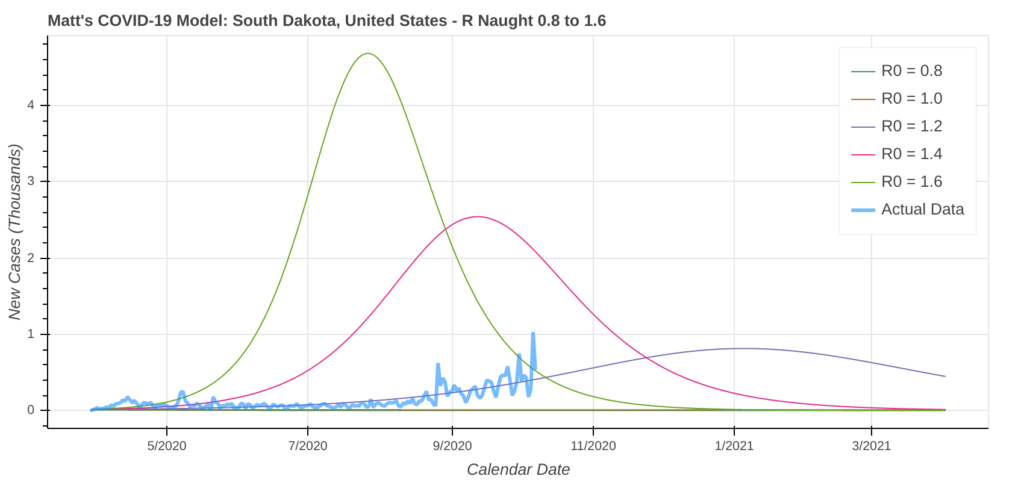
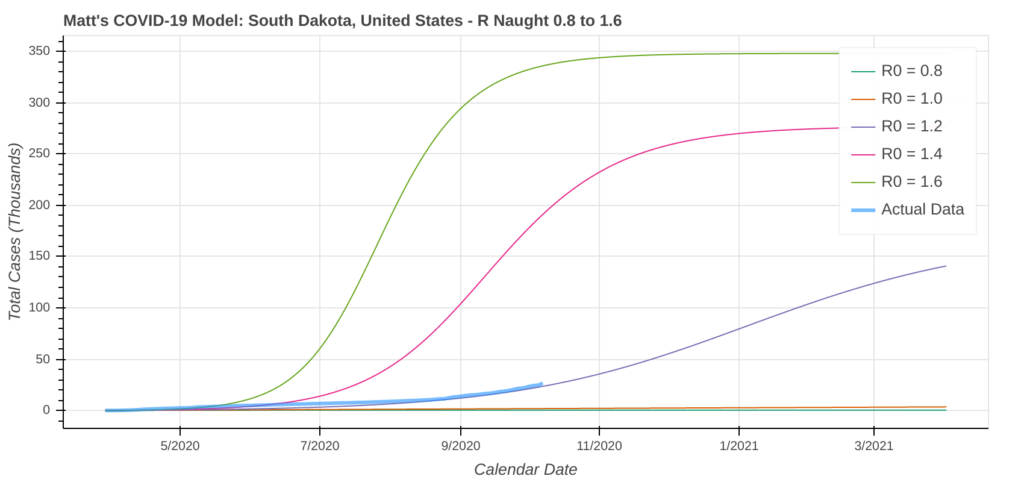
South Dakota
North Dakota may own the highest average number of new cases per capita, but South Dakota just shattered all previous records for the largest single day increase in new cases per capita. Two days ago, South Dakota saw a single-day increase of 1,141 new cases per million people.
COVID-19 is considered under control when that number drops below 50 new cases per million people per day. Like North Dakota, the model’s worst case scenario shows over 60% of South Dakotans contracting COVID-19. That’s up from about 11% just a few weeks ago.
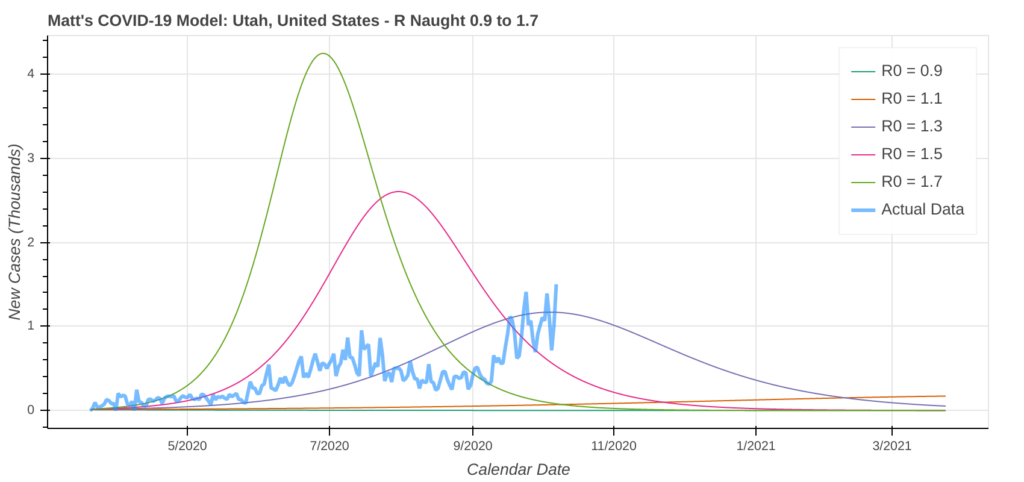
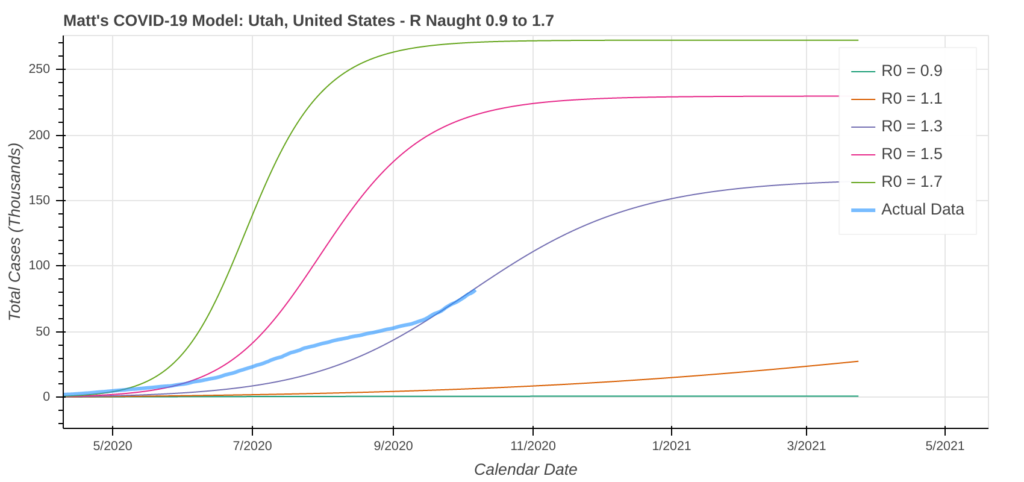
Utah
Cases in Utah have been smoldering throughout the spring and summer, but are starting to burn after a significant acceleration in the rate of spread that started in early September. Without action, I expect that the rate of spread in Utah will not just continue, it will also accelerate.
While it’s unlikely you’ll see a New York-type spike, a surge similar to the one you saw in neighboring Arizona over the summer is certainly possible. Hospital and ICU bed usage is already near record highs. The coronavirus model is currently forecasting that over 12% of Utah’s population could be infected by the end of the pandemic, so you should be taking immediate action to flatten the curve.
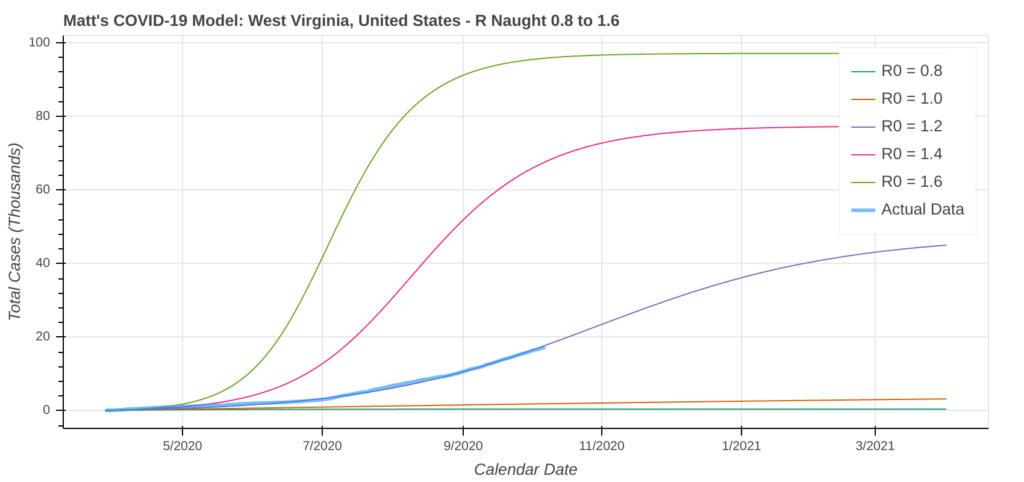
West Virginia
West Virginia is currently in a situation similar to Utah’s, as transmission rates have recently begun to accelerate. The model is showing the potential for a significant outbreak of cases, but the window to prevent such a scenario is till open.
Under the current trajectory, it’s unlikely West Virginia will see a New York or Florida-like spike. The hospital system can handle the current surge, but the virus slowly ripping through the population can still do a lot of damage. The latest model runs show the current surge peaking in early November, infecting at most about 8% of the population.
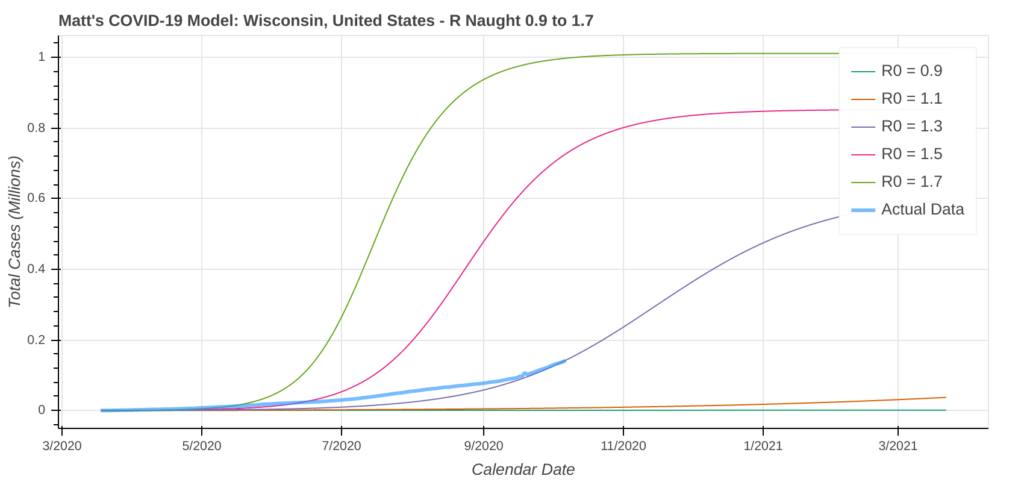
Wisconsin
Of all the states and provinces on this list, I am most concerned about Wisconsin. With a significant outbreak of cases already underway, exponential growth is also accelerating.
Just a couple of weeks ago, the model predicted that only 7% of Wisconsin’s population could become infected. That number has jumped to 25% with the latest model run. At the peak of Florida’s outbreak this summer, the model never predicted more than 9% of Floridians could contract COVID-19.
So why am I so concerned with Wisconsin when both of the Dakotas are showing that up to 60% of their populations could possibly be infected?
- With 5.9 million residents, Wisconsin’s population is over 3.5 times larger than the populations of North Dakota (760,000) and South Dakota (885,000) combined.
- Wisconsin’s population centers are larger and denser than anywhere in the Dakotas. The coronavirus spreads much easier in those areas.
- Much of Wisconsin’s population lives in close proximity to one of the nation’s largest cities. Chicago is a hub of economic activity, transport, travel, and much more.
- Downtown Chicago sits just 85 km (50 mi) from the Wisconsin State Line, and 150 km (93 mi) from Milwaukee.
- If Wisconsin’s outbreak reaches Chicago, it could spread rapidly to other parts of the United States and the world.
Wyoming
Wyoming is in the same boat as the Dakotas. It’s a low population and low population density state facing a massive, yet slow outbreak of cases. To date, Wyoming’s coronavirus trajectory has been almost identical to South Dakota’s, with a rapid acceleration in transmission rate over the past month or so.
In early September, the model’s worst-case scenarios predicted that about 4% of Wyoming’s population could become infected with COVID-19. Over the past four to five weeks, I have watched that number rapidly rise. As of yesterday’s model run, it had risen to 50%, up from 35% just the week before. It is showing no signs of slowing down.
Other States That Should Be On Alert
After ripping through the northeast and the Sun Belt, the United States’ epicenter has set its sights on the Midwest and the Mississippi River Valley. These outbreaks will now be exacerbated as cooler weather drives people indoors. There is still time to take action to prevent clusters and surges, but these states should be on high alert.
- Arkansas
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Minnesota
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- Oklahoma
Additionally, any state or province with large population centers in the northern US or southern Canada should be on high alert for surges in coronavirus. Cool fall weather driving people indoors is already seeding upticks in cases in many of the following states and provinces.
- Alberta
- British Columbia
- Colorado
- Indiana
- Illinois
- Manitoba
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- New Jersey
- New York
- Pennsylvania
- Ohio
- Washington – both Washington State and the District of Columbia
If you live in the southern half of the US, you are by no means out of the woods. This wave will reach you when cooler weather arrives later this fall. Take the time now to plan and prepare to keep yourself, your loved ones, and your fellow citizens safe.
Conclusion
Infectious disease experts have been warning us since April about the likelihood of a significant wave of coronavirus throughout the fall and winter months. Looking at preliminary data, coupled with predictions from several coronavirus models, it’s becoming increasingly clear that experts’ warnings are coming to fruition and that fall and winter wave may already be underway. Wash your hands often, wear your mask in public, and keep your distance from others, and we’ll get through this together.
Top Photo: View of the Summer Monsoon from a Lookout atop the Mogollon Rim
Payson, Arizona – July, 2017







Pingback:COVID-19 Surge in Europe: How Bad will it Get? - Matthew Gove Blog